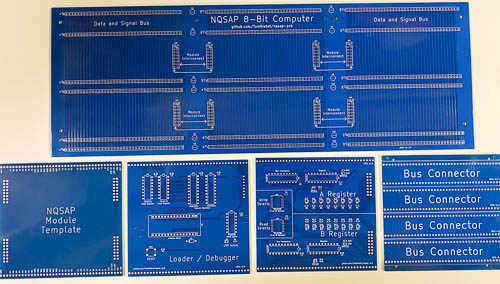
Build 1
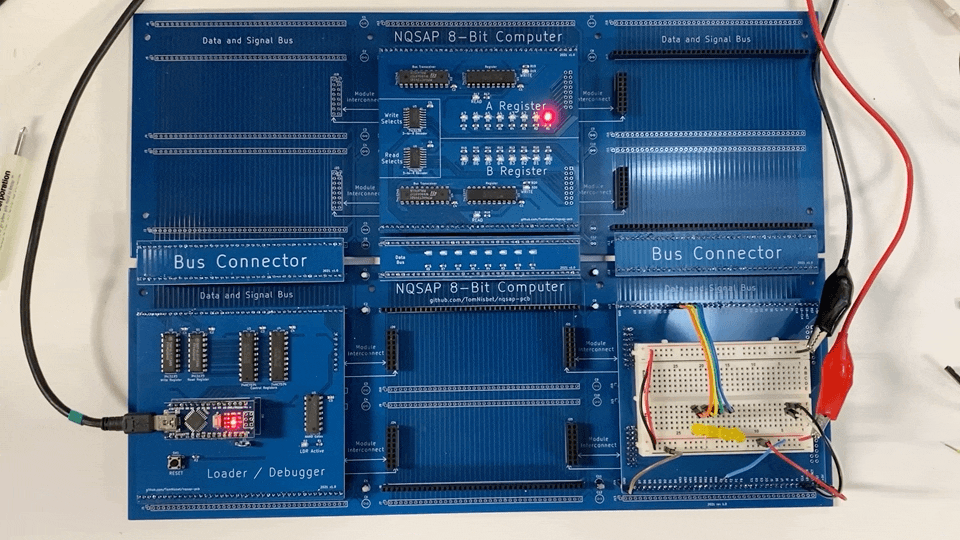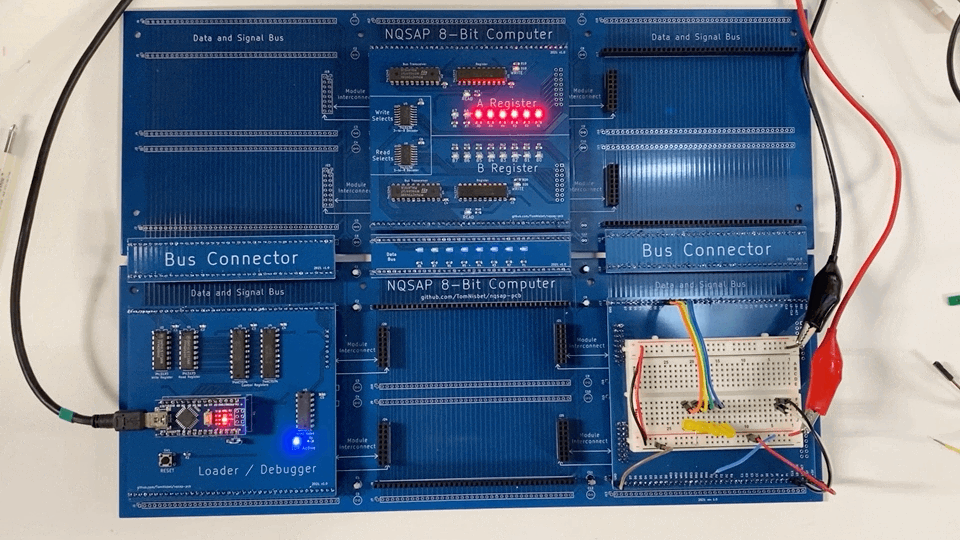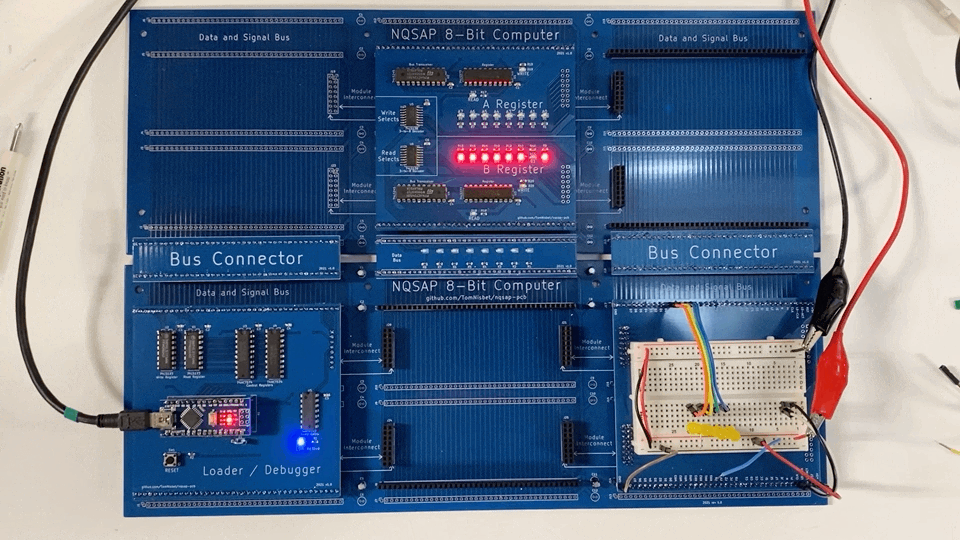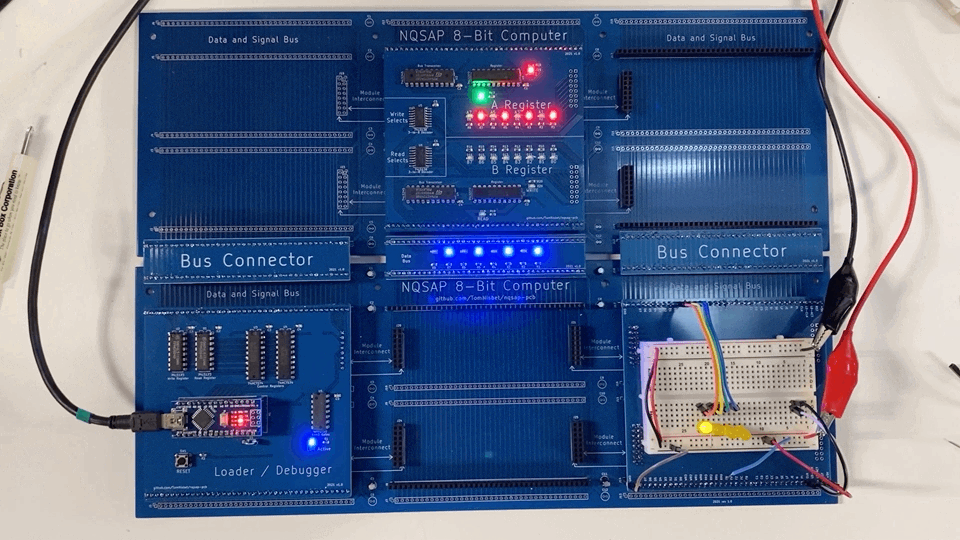
The goal of the initial order of boards was to verify the overall physical and electrical design. The backplane and interconnect boards were designed, along with a few other boards to verify fit and basic functionality.
Backplane and Interconnects
No errors were discovered with the backplane boards. This was fortunate, because these were the most expensive to manufacture. All of the interconnect and module board connections fit perfectly.
The Bus Interconnect boards functioned as designed, but there was some missing silkscreen text that will require a 1.1 version to fix.
Loader
The version 1.0 Loader board worked as designed and was able to test operation of the backplane and the A/B registers. While writing the Loader software, a bus contention issue was discovered that required a hardware change. In addition, the design needed to use two different types of registers for the control signals.
A new design was developed for a version 2.0 board that corrects the bus issue and replaces the four register chips with three shift registers instead. This had the added advantage of simpler wiring and fewer Arduino pins used.
A and B Registers
The A and B registers functioned as designed with no changes required.
A new version will be created when the ALU is completed. This version will add a second output bus transceiver to the B register to implement a right-shift operation.
The original AB Register board mistakenly used a wide SIOC-16 footprint for the 74HCT138 selectors. This required the sourcing of some obscure parts to complete the build. The next version will use a more common footprint, either DIP or SOIC, for the parts.
Template Boards
A blank module board was created to serve as a layout template for all module boards. A set of these boards was included in the first board build. A populated template board was used as a guide when soldering connections onto backplane boards.
A second template was assembled using longer pin connectors. By inserting this template board in place of a module and then using the top pins for breadboard connections, temporary boards can be created that can be plugged in and removed from the system while keeping all of the bus connections to the breadboard intact.